What Are the Causes of ADHD in Adults?
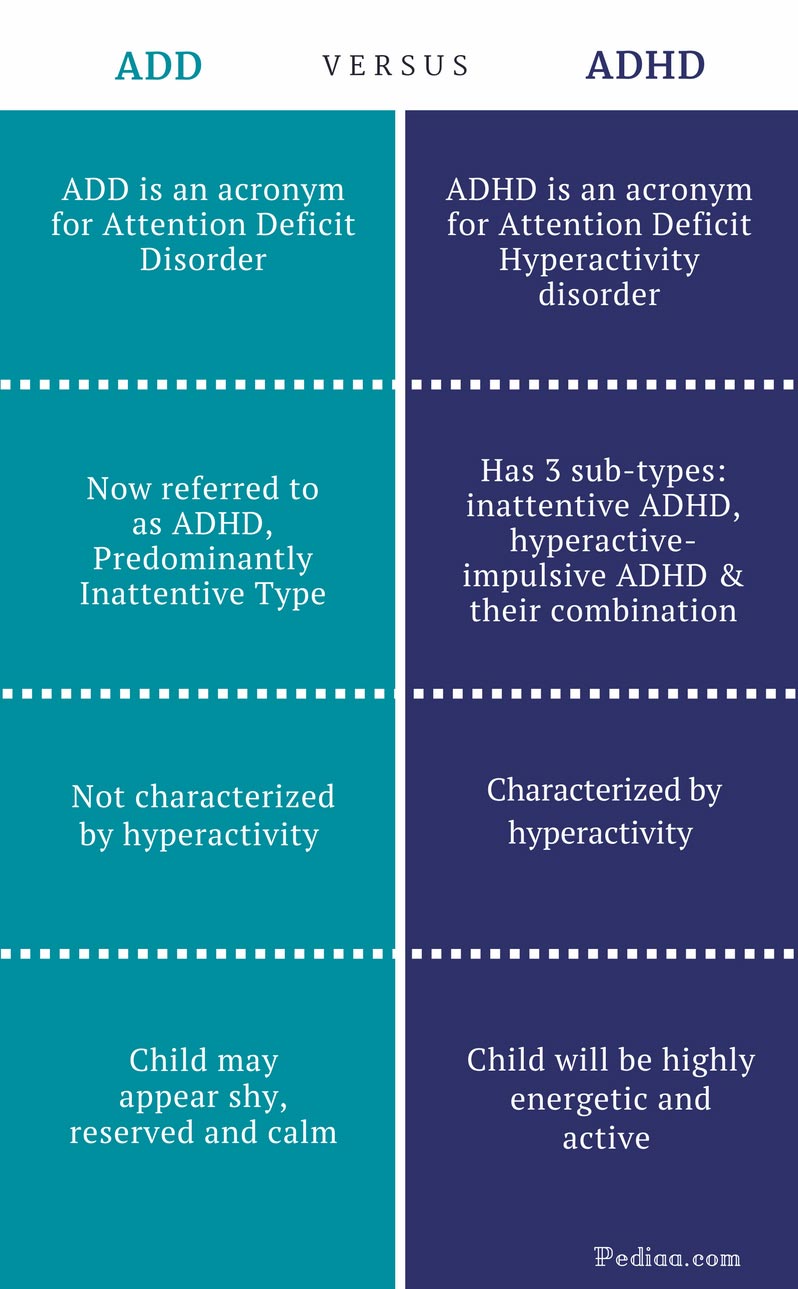
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), also known as ADD, is attention deficit disorder characterized by hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in adults, also known as ADD in adults, is a neuropsychological disorder that involves a combination of persistent difficulties, including lack of concentration, impulsivity, and poor focus. ADHD in adults is associated with other psychological disorders such as substance abuse and other mental illnesses. ADHD in adults can cause a variety of problems, including unstable relationships, low grades, and poor school performance, all of which are associated with poor social interaction and bad relationships. The symptoms of ADHD in adults are almost identical to children, but adults can have more severe symptoms and a wider range of disorders.
Adults with ADHD are often seen as lazy, irresponsible, unmotivated, and less conscious than most people, although these traits are not reflected in their appearance. They are also more likely to suffer from depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. These problems are often associated with the impulsivity and inattention that are common in adults with ADHD. These symptoms of ADHD in adults have led to several treatments and drug development.
Most of the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder are caused by genetic and neurological dysfunctions. Because the symptoms of ADHD in adults are very similar to those of children, it was difficult to determine whether they were caused by one of these factors or another disorder or condition. Many children with ADHD perform well in school, while many adults are in the same situation but with lower grades. One of the main causes of ADHD in adults is an imbalance in the levels of dopamine in the brain, a neurotransmitter that controls impulsivity, attention, memory, and emotions.
Several medications have been developed specifically to treat the symptoms of ADHD in adults
These medicines can have unwanted side effects, and most doctors choose to use these alternatives. Psychotherapy, especially when treating ADHD symptoms, is usually the preferred treatment for adults. These medications are used as adjunctive therapy, along with counseling and group sessions. In recent years, psychostimulants, stimulants (Ritalin, Adderall, Dexedrine) and atomoxetine have been used in combination with behavioral therapy. for the treatment of ADHD symptoms in adults. For more information on disease and disease treatment, see website.
Medication for ADHD in adults is usually only used when a child or adult has a particularly severe case of ADHD, when symptoms are not limited to inattention and hyperactivity. However, these medications are also prescribed to reduce symptoms in the absence of ADHD. They are also sometimes prescribed for the treatment of comorbid conditions of depression and anxiety. It is important to remember that the effect of medications depends on the age and severity of the symptoms. Some adults require two to three months of treatment before any behavioral improvement is noticeable, and this period of time may be lengthened if the side effects of the medication are severe.
If symptoms of ADHD in adults are mild to moderate, many doctors take a less aggressive approach and recommend a combination of these alternatives rather than prescribing medications. The first step is to introduce the child or adult to various strategies that will improve social interaction, reduce the child’s or adult’s impulsivity, and improve their concentration.
After a patient has taken medication to treat ADHD symptoms, the doctor may add a behavior modification program, cognitive behavioral therapy, or family therapy to help manage the symptoms. They can also use medicines as an adjunct to this treatment.
