A Brief Introduction to Addisons Disease
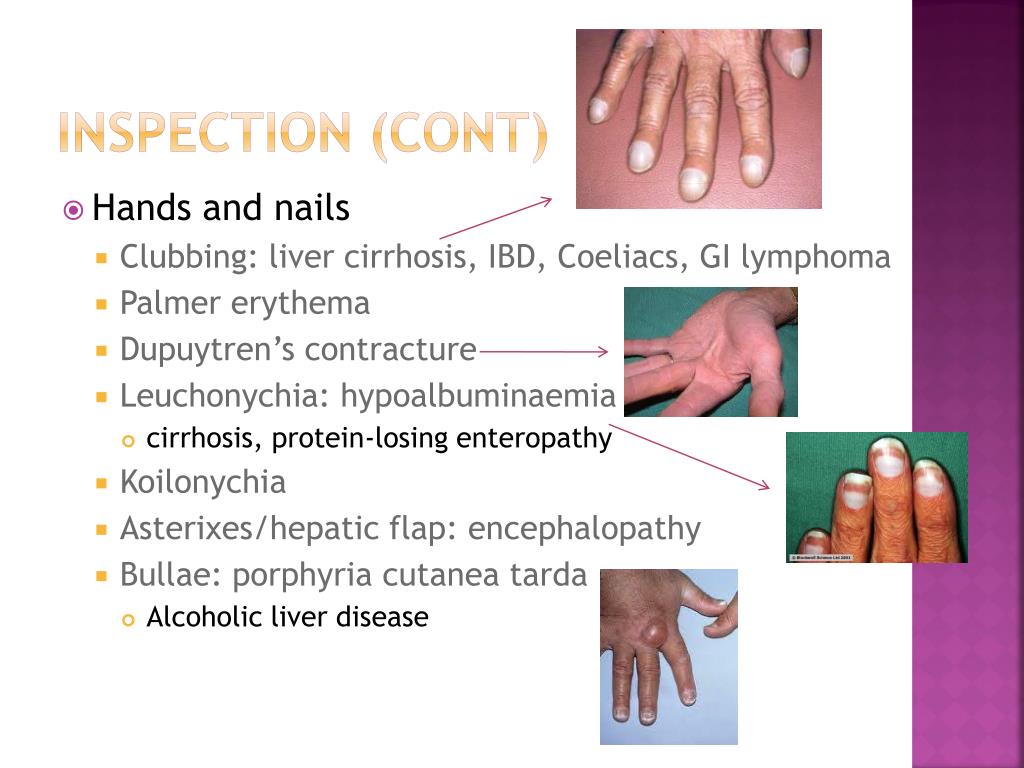
Primary adrenal insufficiency is called Addison's disease or adrenal cortex insufficiency. This condition occurs when the adrenal glands are damaged or limited in function. They usually produce enough stress-releasing hormone, cortisol, in response to adrenaline, adrenaline. When the adrenal glands are not functioning well, the brain feels the need for more and therefore releases more of these chemicals. This isn't always a problem, as excess cortisol helps keep the body healthy. However, Addison's disease usually occurs due to an overactive adrenal gland. There is often a decrease in adrenaline levels, which can cause pain and weakness, digestive problems, depression, and weight loss.
Addison's disease can occur at any stage of life, but usually appears before the age of 30. The exact reason is unknown. It can happen in adults or children. Other possible causes include cancer, diabetes, excess thyroid hormones, and certain medications. In some cases, it can be caused by an attack by the autoimmune system of the adrenal glands, which is called primary adrenal toxicity.
Symptoms of Addison's disease include weight loss, depression, fever, hot flashes, muscle weakness, and fatigue. The most common Addison treatment is corticosteroids. They are used for short-term relief, but the side effects can be serious. They also have many unwanted interactions with other medications.
Other forms of Addison's disease include juvenile hyperinsulinemia and Addison's syndrome. Juvenile hyperinsulinemia occurs when an overproduction of insulin occurs in the body. People with juvenile hyperinsulinemia usually have higher-than-normal glucose levels and high cholesterol levels. People with Addison's disease usually have these two conditions.
Addison's syndrome occurs when a person has low insulin sensitivity, but the body still produces enough hormone to provide energy. The condition is associated with Addison's disease. Addison's symptoms are the same as for Addison's disease, but include fatigue, fatigue, nausea, and depression. However, with Addison's syndrome, the skin and joints are very dry and cracked.
If Addison is left untreated, it can lead to Addison's disease. It is a dangerous condition that occurs when there is too much cortisol in the body. This can lead to organ failure or organ necrosis. This can cause kidney damage and death. There are ways to prevent Addison's disease from progressing to Addison's disease.
There are treatments for Addison's disease. Corticosteroids are one such drug. These medications can help regulate cortisol production as well as improve pancreatic function. Corticosteroids can help reduce pain and improve liver function, and in many cases, they can boost the immune system. Corticosteroid therapy should only be started after all other treatments have been tried.
Some doctors recommend surgery while others do not. If you suspect you have Addison's disease, talk with your doctor about the course of treatment
Corticosteroids are usually injected into the underarm area. They work by blocking adrenal receptors in your body. This blocks the production of cortisol, which in turn helps regulate the normal functioning of your body. Corticosteroids should not be used for a long time, as they have a negative effect on the liver.
Long-term use of corticosteroids can cause nausea, vomiting, and weight gain. You may also experience weakness, loss of appetite, and nausea. If you are taking any oral contraceptives or blood pressure medications, you should stop taking them before starting any therapy. for Addison's disease. If you have a family history of the condition, you should also be screened for cancer and heart disease.
If Addison's disease is left untreated, it can develop into Addison's disease. This is a more serious disease that occurs when the amount of dopamine in the brain decreases, which can be caused by Addison's disease itself. As Addison's disease progresses, dopamine levels begin to decline. Patients with Addison's dementia may begin to show signs of depression, memory loss, thinking problems, speech problems, personality changes, and confusion. Medication is sometimes prescribed to control these symptoms.
Treatment for Addison's disease depends on the cause of the disease. Corticosteroids are the most common option.
